What is Acrylic?
Acrylic, scientifically known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is a synthetic polymer derived from the distillation of acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, or their derivatives. This plastic material is renowned for its clarity, weather resistance, and high tensile and impact strength, making it a popular alternative to glass. Acrylic is lightweight, shatter-resistant, and provides excellent light transmission, which is why it is commonly used in windows, skylights, and outdoor signs. It can be easily colored, molded, cut, drilled, and formed, offering versatility in various applications from art installations to automotive tail lights.
What is Plexiglass?
Plexiglass is a brand name for acrylic (PMMA) and shares the same basic material properties. The name “Plexiglass” comes from one of the original and most well-known manufacturers of acrylic sheets. This material is famed for its glass-like clarity and is often used where transparency is required, alongside the need for higher impact resistance than glass offers. Common uses of Plexiglass include protective barriers, picture framing, and secondary glazing. Its ability to be easily fabricated and its resistance to UV light and weather conditions make it a preferred choice for both indoor and outdoor applications.
What is Lexan?
Lexan is a brand name for polycarbonate, a different type of thermoplastic that is noted for its exceptional impact resistance, toughness, and heat resistance. Developed originally by General Electric Plastics (now SABIC), Lexan is often chosen for applications where safety and performance under stress are crucial. Unlike acrylic, Lexan can withstand significant deformations without breaking, making it ideal for bullet-proof windows, eyewear lenses, and as protective covers in high-risk environments. Its versatility extends to automotive components, medical devices, and electronic cases, where durability is critical. Lexan is also more resistant to temperature extremes and has a slightly higher price point compared to acrylic materials.
What is the Main Difference Between Acrylic and Plexiglass?
The main difference between Acrylic and Plexiglass is that Plexiglass is essentially a brand name of acrylic. Acrylic refers to polymers derived from acrylic acid or methacrylic acid, specifically polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). Plexiglass, on the other hand, is a popular trade name used by many manufacturers for their specific variety of acrylic sheets. Essentially, all Plexiglass is acrylic, but not all acrylic is Plexiglass. This distinction is similar to the relationship between tissue and Kleenex, where the brand name becomes synonymous with the product itself.
What is the Main Difference Between Plexiglass and Lexan?
The main difference between Plexiglass and Lexan is that Lexan is a brand name for polycarbonate, a different type of thermoplastic polymer, while Plexiglass is a brand of acrylic (PMMA). Lexan is known for its extraordinary strength and impact resistance, considerably higher than acrylic materials, including Plexiglass. This makes Lexan a preferred material in applications where safety and durability are critical, such as in bullet-resistant windows, whereas Plexiglass is often used where aesthetics are more important, like in advertising displays.
What is the Main Difference Between Acrylic and Lexan?
The main difference between Acrylic and Lexan is that acrylic is less durable and impact-resistant than Lexan. Acrylic, including brands like Plexiglass, is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. Lexan, which refers to a specific type of polycarbonate, is tougher and more resilient against impacts and harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for more demanding applications such as protective gear and outdoor enclosures.
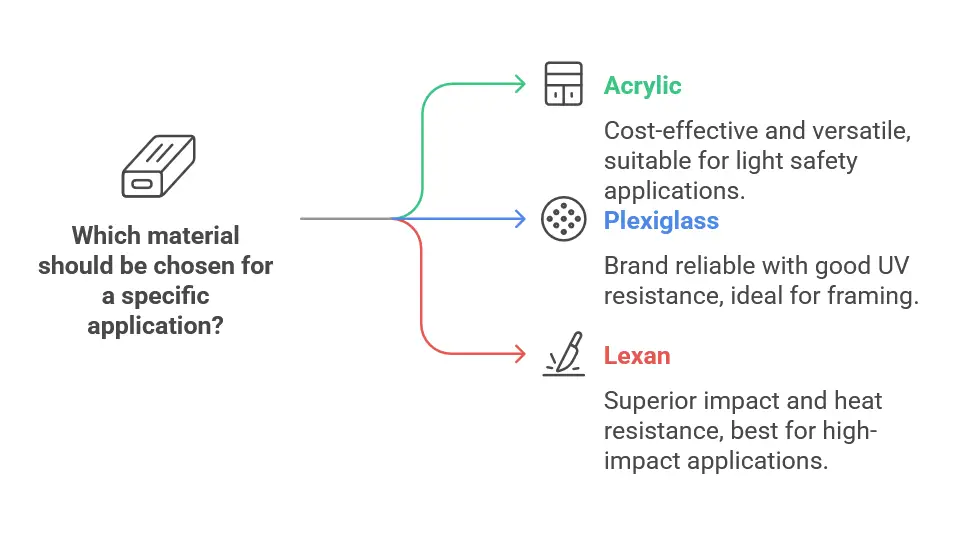
Features of Acrylic vs Plexiglass vs Lexan
- Material Composition: Acrylic and Plexiglass are both forms of PMMA, sharing similar properties such as light transmission and UV resistance, whereas Lexan is a polycarbonate with superior impact resistance and flexibility.
- Impact Resistance: Acrylic offers moderate impact resistance, Plexiglass provides slightly enhanced resistance, and Lexan stands out with the highest resistance, suitable for highly demanding applications.
- Flexibility: Acrylic is less flexible than both Plexiglass and Lexan, with Lexan being the most flexible, allowing for applications requiring significant bending and shaping.
- Heat Resistance: Lexan surpasses both acrylic and Plexiglass in heat resistance, making it ideal for environments exposed to high temperatures.
- Price Point: Generally, acrylic is the most economical, followed by Plexiglass, with Lexan being the most expensive due to its advanced material properties.
- Scratch Resistance: Acrylic and Plexiglass are more prone to scratches compared to Lexan, which offers a harder surface more resistant to wear and tear.
- UV Stability: All three materials provide UV resistance, but acrylic and Plexiglass are particularly favored for applications where minimal UV-induced degradation is crucial.
Key differences between Acrylic and Plexiglass
- Brand and Generic Terminology: Acrylic is the generic term used to describe PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), whereas Plexiglass is a specific brand of acrylic. This is akin to the difference between aspirin and Bayer.
- Availability and Variety: While all Plexiglass is made of acrylic, not all acrylic sheets available on the market are Plexiglass. Acrylic can be found under various brand names which may differ slightly in terms of formulations and properties.
- Price Points: Generally, Plexiglass, being a branded product, can be priced slightly higher than generic acrylic products, which do not carry the brand name premium.
- Market Perception: Plexiglass is often perceived as a higher-quality product compared to standard acrylic due to its brand recognition. This perception can influence buyer choice, especially in markets where branding is a significant factor.
- Quality Consistency: As a branded product, Plexiglass often has stringent manufacturing quality controls, potentially leading to more consistent quality across different batches compared to generic acrylic products.
- Availability of Product Information: Plexiglass, being a branded product, usually comes with detailed product specifications and usage guidelines, which might not always be as readily available for generic acrylic.
- Consumer Recognition: Due to extensive marketing and longevity in the market, Plexiglass enjoys higher consumer recognition compared to generic acrylic sheets, which might be marketed under less familiar brand names.
Key similarities between Acrylic and Plexiglass
- Material Composition: Both Acrylic and Plexiglass are made from polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), sharing the same chemical composition and basic material properties.
- Transparency: Both materials are highly valued for their clarity and transparency, often being used as a lightweight and shatter-resistant alternative to glass.
- Fabrication Flexibility: Acrylic and Plexiglass can both be easily cut, drilled, formed, and molded, making them versatile for various applications, from art installations to architectural features.
- UV Resistance: Both materials offer good resistance to UV light, making them suitable for outdoor applications without significant yellowing or degradation over time.
- Impact Resistance: Although not as tough as polycarbonate, both Acrylic and Plexiglass offer higher impact resistance compared to traditional glass.
- Applications: The uses of both Acrylic and Plexiglass overlap significantly, found in applications such as protective barriers, displays, signage, and light fixtures.
Key differences between Plexiglass and Lexan
- Chemical Composition: Plexiglass is made from PMMA, whereas Lexan is a brand of polycarbonate, a different type of plastic with distinct chemical properties.
- Impact Resistance: Lexan exhibits superior impact resistance and is less likely to crack or shatter compared to Plexiglass, making it suitable for more demanding safety applications.
- Heat Resistance: Lexan can withstand higher temperatures and has a higher melting point compared to Plexiglass, enhancing its suitability in environments exposed to high heat.
- Optical Clarity: While both materials are clear, Plexiglass tends to have a slight edge in optical clarity under certain conditions, though Lexan is close in performance.
- Price Comparison: Typically, Lexan is more expensive than Plexiglass due to its advanced durability and performance characteristics.
- Flexibility and Bendability: Lexan is more flexible than Plexiglass and can be bent or molded at room temperature without cracking, offering advantages in certain fabrication processes.
Key similarities between Plexiglass and Lexan
- Transparency and Light Transmission: Both materials offer high levels of transparency and are excellent for applications requiring clear visibility.
- Weather Resistance: Both Plexiglass and Lexan are resistant to weather elements, including UV radiation and moisture, making them suitable for outdoor use.
- Versatility: Each material can be used in a variety of applications, from automotive to architectural, demonstrating their adaptability.
- Machinability: Both materials can be cut, drilled, and shaped using standard tools, making them easy to work with in manufacturing and DIY projects.
- Maintenance: Both Plexiglass and Lexan are easy to clean and maintain, requiring only basic care to keep them looking clear and polished.
- Safety Features: Both materials are used in safety applications due to their impact resistance (though to varying degrees), providing protection against breakage.
Key differences between Acrylic and Lexan
- Material Strength: Lexan is significantly stronger and more impact-resistant than acrylic, making it suitable for more demanding applications where durability is critical.
- Flexibility: Lexan is more flexible than acrylic and can withstand deformations that would typically crack or break acrylic.
- Heat Resistance: Lexan can tolerate higher temperatures and has a higher resistance to heat compared to acrylic, expanding its uses in environments exposed to heat.
- Cost Considerations: Generally, Lexan is more expensive than acrylic due to its superior properties and performance.
- Scratch Resistance: Acrylic is softer and more prone to scratches compared to Lexan, which is harder and more resistant to surface damage.
- Chemical Resistance: Lexan generally has better resistance to chemicals and solvents compared to acrylic, making it more suitable in industrial applications.
Key similarities between Acrylic and Lexan
- Light Transmission: Both materials are highly transparent and are excellent alternatives to glass in terms of light transmission.
- Weatherability: Acrylic and Lexan are both durable against weather conditions, including UV exposure and temperature fluctuations.
- Applications: Both are used in a wide range of applications, from automotive components to protective coverings.
- Formability: Both materials can be thermoformed and machined to specific shapes and sizes, providing flexibility in design and use.
- Safety: Both materials are preferred over glass in safety-sensitive areas due to their higher impact resistance and shatterproof nature.
- Maintenance: Acrylic and Lexan are both easy to maintain, requiring only regular cleaning with mild detergents to maintain clarity and performance.
Pros of Acrylic Over Plexiglass and Lexan
- Cost-effectiveness: Generally, acrylic is more affordable than both Plexiglass and Lexan, making it an economical choice for projects with budget constraints.
- Ease of fabrication: Acrylic can be easily manipulated through processes like laser cutting, bending, and gluing, which is particularly advantageous for custom designs and applications.
- Weight advantage: Acrylic is lighter than Lexan, which can be a critical factor in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in automotive or aerospace components.
- Color variety: Acrylic comes in a wider range of colors and finishes compared to Plexiglass and Lexan, offering more flexibility in aesthetic design choices for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Scratch resistance: When compared to Plexiglass, standard acrylic sheets tend to have a harder surface, which makes them more resistant to scratches.
- UV stability: Acrylic has excellent resistance to UV light, surpassing Lexan in environments where prolonged exposure to sunlight is a factor, thus maintaining clarity and resisting yellowing over time.
- Transparency: Acrylic provides exceptional optical clarity, often outperforming Lexan in applications where a glass-like appearance is desired.
Cons of Acrylic Compared to Plexiglass and Lexan
- Impact resistance: Acrylic is more brittle and susceptible to cracking under impact compared to both Plexiglass and Lexan, which may be a drawback in high-risk environments.
- Heat resistance: Acrylic has a lower heat resistance than Lexan, limiting its use in applications where high temperatures are prevalent.
- Flexibility: Unlike Lexan, acrylic is less flexible, which can limit its use in applications that require material bending or shaping at room temperature.
- Chemical sensitivity: Acrylic is more prone to damage from certain chemicals and solvents compared to Lexan, requiring careful consideration of environmental factors in its application.
- Durability under stress: Under conditions of stress and impact, acrylic is more likely to shatter than Lexan, which is built to endure more extreme conditions.
- Longevity: In demanding industrial applications, acrylic may not perform as well as Lexan in terms of longevity and durability, necessitating more frequent replacement or maintenance.
Pros of Plexiglass Over Acrylic and Lexan
- Brand recognition: Plexiglass, being a well-established brand, is often associated with high-quality standards and reliability, which can influence purchasing decisions and consumer trust.
- Optical clarity: Plexiglass is known for its superior optical clarity, often outperforming both acrylic and Lexan in applications requiring crystal-clear transparency.
- UV resistance: Plexiglass offers excellent resistance to UV degradation, making it ideal for outdoor applications where long-term exposure to sunlight is expected.
- Impact resistance: While not as impact-resistant as Lexan, Plexiglass offers greater resistance to breakage compared to standard acrylic, suitable for moderate safety applications.
- Scratch resistance: Plexiglass sheets tend to be more resistant to scratches compared to standard acrylic, maintaining a clearer surface over time.
- Fabrication versatility: Plexiglass can be easily fabricated and molded, similar to acrylic, allowing for its use in a wide range of custom applications.
- Aesthetic quality: The brand often ensures a consistent aesthetic quality that is crucial for applications like display cases and framing where visual appearance is key.
Cons of Plexiglass Compared to Acrylic and Lexan
- Cost factor: Plexiglass generally comes at a higher cost compared to standard acrylic due to its branding and perceived quality, which may not be justifiable for all project budgets.
- Flexibility limitations: Compared to Lexan, Plexiglass is less flexible, which can restrict its use in applications that require bending or shaping without heating.
- Weight: Plexiglass is heavier than standard acrylic, which might be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a critical factor.
- Heat sensitivity: Although it has good heat resistance, Plexiglass may not perform as well as Lexan in high-temperature environments, limiting its application scope.
- Chemical resistance: While better than acrylic, Plexiglass is still more susceptible to certain chemicals compared to Lexan, requiring careful consideration in chemically exposed environments.
- Impact durability: Despite being tougher than standard acrylic, Plexiglass still lags behind Lexan in terms of impact resistance and durability in extremely harsh conditions.
Pros of Lexan Over Acrylic and Plexiglass
- Higher Impact Resistance: Lexan is significantly more impact-resistant than both acrylic and Plexiglass. This property makes it an ideal choice for safety-centric applications such as bullet-resistant windows and protective face shields.
- Enhanced Durability: Due to its tough chemical composition, Lexan exhibits better resistance to breaking and cracking under stress compared to acrylic and Plexiglass. This durability extends the lifespan of products made with Lexan, especially in harsh environmental conditions.
- Greater Flexibility: Lexan sheets are more flexible than those made of acrylic and Plexiglass, allowing them to be used in applications requiring bending and shaping without the risk of cracking.
- Higher Temperature Resistance: Lexan withstands higher temperatures and has a better thermal stability than acrylic and Plexiglass. This makes it suitable for applications near heat sources or outdoors where high temperatures can be a concern.
- Less Prone to Scratching: While all clear plastics will scratch, Lexan is harder and more resistant to surface scratches compared to acrylic and Plexiglass. This makes it more suitable for high-traffic areas or where surface wear is a concern.
- Better Chemical Resistance: Lexan has a higher resistance to chemicals, including various acids and hydrocarbons, which can cause damage to acrylic and Plexiglass. This chemical resistance is crucial in industrial settings where exposure to solvents and other chemicals is common.
- UV Resistance and Stability: Although all three materials offer UV resistance, Lexan maintains its clarity and resistance over longer periods and under more intense UV exposure. This stability helps prevent yellowing and degradation, ensuring long-term performance in outdoor settings.
Cons of Lexan Compared to Acrylic and Plexiglass
- Higher Cost: The superior properties of Lexan come at a higher price point compared to acrylic and Plexiglass. This can be a limiting factor for budget-sensitive projects where cost is a critical consideration.
- Reduced Optical Clarity: While Lexan is highly transparent, it does not match the optical clarity of Plexiglass, which can be a disadvantage in applications where aesthetic appearance and clear visibility are paramount.
- More Difficult to Process: Lexan’s toughness and resistance make it more challenging to cut and drill compared to acrylic and Plexiglass. Specialized tools and techniques may be required, potentially increasing fabrication costs.
- Heavier Weight: Lexan is denser and therefore heavier than acrylic and Plexiglass. This increased weight can be a disadvantage in applications where lightweight materials are preferred, such as in some framing or display installations.
- Potential for Stress Cracking: Although Lexan is generally more flexible, it can be susceptible to stress cracking when exposed to certain chemicals or stressed during installation. This requires careful handling and proper installation techniques to prevent damage.
- Thermal Expansion: Lexan experiences greater thermal expansion compared to acrylic and Plexiglass. In applications involving large panels or where materials are subject to temperature fluctuations, this can lead to issues with fitting and maintaining seals.
- Limited Acrylic Adhesives Compatibility: Due to its chemical composition, Lexan may not be compatible with certain acrylic adhesives used for Plexiglass. This can limit the options available for bonding or require the use of more expensive specialized adhesives.
Situations when Acrylic is Better than Plexiglass and Lexan
- Cost Efficiency: Acrylic is generally more affordable than Plexiglass and Lexan, making it a cost-effective option for large-scale installations or for budget-conscious projects.
- Ease of Handling and Fabrication: Acrylic can be easily cut, drilled, and shaped, offering a distinct advantage in custom fabrication projects over the more rigid and tough Lexan.
- Color and Finish Options: Acrylic offers a broader range of colors and finishes, allowing for greater creative flexibility in design-focused applications such as interior decor or artistic installations.
- Weight Considerations: Acrylic is lighter than Lexan, which can be crucial for applications where weight is a significant concern, such as in mobile or hanging installations.
- UV Resistance: Acrylic exhibits superior resistance to UV light degradation compared to Lexan, maintaining clarity and color stability longer in sun-exposed environments.
- Optical Clarity: In applications where the utmost clarity is required, acrylic provides a glass-like transparency that is often preferred over the slight tint that can be present in Lexan.
- Scratch Resistance: Compared to Plexiglass, standard acrylic sheets are harder and more resistant to scratches, which is beneficial in high-traffic areas or in applications where surface aesthetics are important.
Situations when Plexiglass is Better than Acrylic and Lexan
- Brand Trust and Quality Assurance: Plexiglass, being a recognized brand, often guarantees a consistent quality that is trusted by consumers and professionals alike, making it preferable in high-end applications.
- Impact Resistance: While not as strong as Lexan, Plexiglass offers better impact resistance compared to standard acrylic, making it suitable for use in moderate safety applications like protective barriers.
- Optical Clarity Over Acrylic: Plexiglass generally offers better optical clarity than standard acrylic, making it ideal for applications such as photography framing or where fine detail visibility is crucial.
- UV Stability: Plexiglass has excellent resistance to UV light, outperforming both acrylic in maintaining transparency and integrity when exposed to sunlight for prolonged periods.
- Aesthetic Consistency: For projects requiring a visually appealing finish, such as display cases or retail fixtures, Plexiglass provides a consistently clear and high-quality appearance.
- Fabrication Flexibility: Like acrylic, Plexiglass can be easily fabricated and molded, yet it holds its form slightly better under stress, beneficial for precision manufacturing needs.
- Scratch Resistance: Plexiglass surfaces are more resistant to scratches compared to standard acrylic, maintaining a clear and polished appearance over longer periods.
Situations when Lexan is Better than Acrylic and Plexiglass
- High Impact Applications: Lexan’s superior impact resistance makes it the best choice for safety-critical applications such as bullet-resistant windows or protective gear.
- Durability in Harsh Conditions: Lexan’s toughness makes it ideal for use in environments with extreme conditions, such as outdoor enclosures that face harsh weather or mechanical stresses.
- Flexibility for Complex Shapes: The flexibility of Lexan allows it to be used in applications requiring material bending or shaping without the risk of breaking, such as in custom automotive components.
- High Temperature Environments: Lexan’s ability to withstand higher temperatures makes it suitable for applications near heat sources, such as industrial lighting fixtures or mechanical parts.
- Chemical Resistance: Lexan offers better resistance to chemicals and solvents compared to acrylic and Plexiglass, making it preferable in industrial settings where chemical exposure is a concern.
- Long-term UV Exposure: Lexan maintains its structural integrity and clarity better than acrylic and Plexiglass in prolonged UV exposure scenarios, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
- Reduced Yellowing Over Time: Lexan is less prone to yellowing compared to acrylic and Plexiglass, ensuring that it remains clear and effective for visibility and aesthetic purposes over time.
Comparison Table: Acrylic vs Plexiglass vs Lexan
| Feature/Aspect | Acrylic | Plexiglass | Lexan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | PMMA | PMMA (specific brand) | Polycarbonate |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Higher than Acrylic | Highest among the three |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | Less flexible than Lexan | Most flexible |
| Heat Resistance | Lower than Lexan | Higher than Acrylic, lower than Lexan | Highest |
| Price Point | Most economical | Higher due to brand premium | Most expensive |
| Scratch Resistance | More prone to scratches | More resistant than Acrylic | Best scratch resistance |
| UV Stability | Excellent | Excellent | Good, best long-term stability |
| Optical Clarity | High | Highest | Slightly less than Plexiglass |
| Chemical Resistance | Less resistant | Better than Acrylic, less than Lexan | Best resistance |
| Durability & Longevity | Less durable than Lexan | More durable than Acrylic, less than Lexan | Most durable |
| Weight | Lighter than Lexan | Heavier than Acrylic | Heaviest |
| Ease of Fabrication | Easiest to handle and fabricate | Easy, similar to Acrylic | Requires special tools and techniques |
| Applications | Light safety applications, displays | Moderate safety applications, framing | High-impact applications, harsh conditions |
| Pros | Cost-effective, versatile in color & shape | Brand reliability, better UV resistance | Superior impact and heat resistance |
| Cons | Less impact and heat resistance | Cost, less flexibility | Higher cost, reduced optical clarity |